| PerfectRouter.com DD-WRT Router Tutorial |
What is DD-WRT?
DD-WRT is a Linux-based firmware for several wireless routers, most notably the Linksys WRT54G series. Like other similar projects, DD-WRT is considered a third-party firmware solution designed to replace the firmware that ships pre-installed on many commercial routers. This is done for a variety of reasons; including but not limited to the addition of features which are not typically included in a manufacturer's router firmware.
Initial setup of a DD-WRT router
DD-WRT routers, unlike an off-the-shelf router, typically require at least a little configuration before regular usage.
A DD-WRT router does not use an install CD, and instead configuration is done through a setup web page hosted on the router itself.
To set a DD-WRT router up, first plug in the power. Wait a moment, at least 10 seconds or until the power light stops flashing, then either connect to the wireless network 'dd-wrt' or connect an ethernet cable to one of the four switch ports on the back of the device. Now that the unit is powered up and your connected to it you can visit the configuration page in a web browser. It is typically best to clear your browsers cache before viewing the page, and it typically works best in Google Chrome or Internet Explorer. To get to the setup page type http://192.168.1.1 into the address bar.
The initial setup page is shown below:
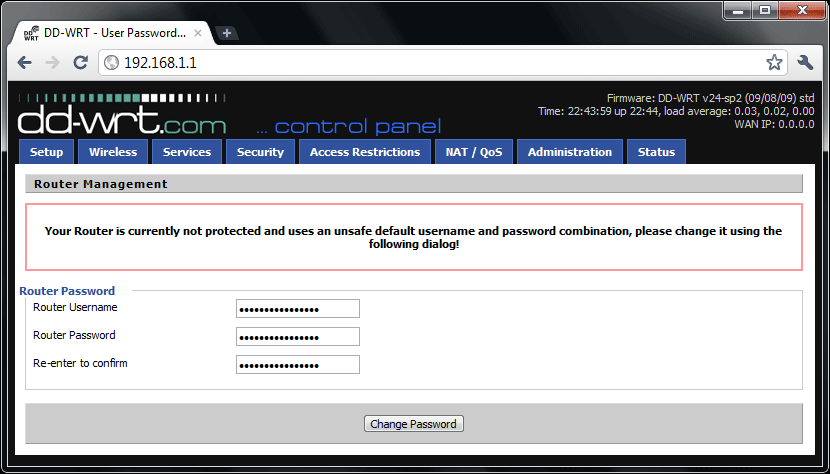
When you first visit the DD-WRT setup page you will be prompted to create a username and password. This username and password are to protect access to the setup page so that only someone who knows the username and password can change settings on the router.
Once a username and password are created you will be sent to the Status>Sys Info page. This is where you can see what devices are connected to the router, and information about network connectivity and resource usage. This is the only page visible without entering a username and password. The Status>Sys Info page for our example router is shown below.
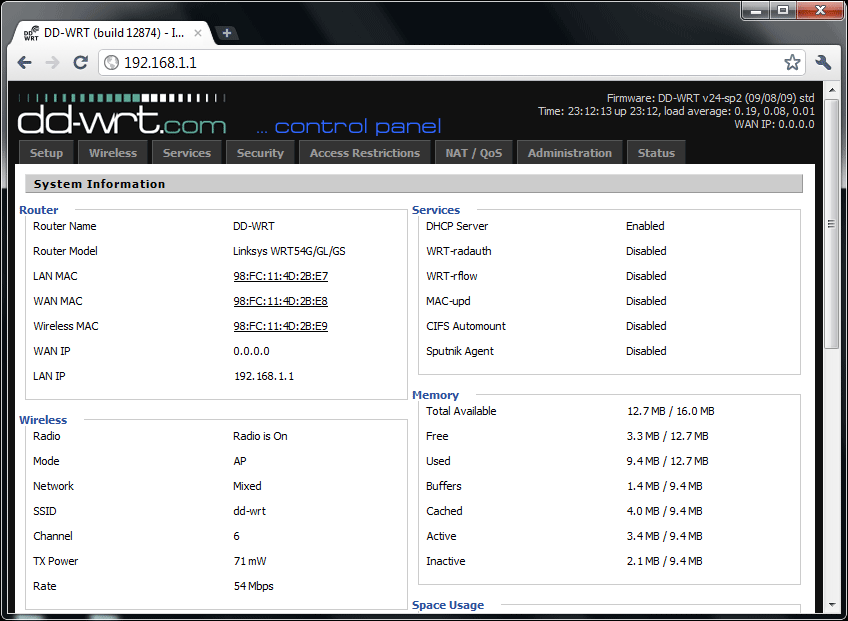
You can also disable any page from being shown without a username and password under Administration>Management>Info Site Password Protection
Once you try to visit one of the tabs you will be prompted for a username and password. This is the username and password you just created to protect the setup page. Once this is entered you can browse the various configuration pages.
What settings to change for various implementations are covered in the links at the top of the page under Broadcom and Atheros.
Common DD-WRT Implementations
The most common implementation is AP or Access Point. This is the typical role of a wireless router, to provide both wireless access to devices such as laptops and wired access to desktop computers through the switch ports. This mode is used when you have a DSL or cable internet connection. For this implementation you connect an ethernet cable from your modem to the internet port on your DD-WRT router.
The second most common implementation is using the DD-WRT router to pull in a distant signal that is too faint for a laptop to connect to reliably. This signal is then 'repeated' by the DD-WRT router with your own wireless network name (SSID). Connectivity to the distant network is provided through the DD-WRT router's switch ports as well so that desktops without wireless can use the resources of the distant wireless network. This repeater mode is often used to extend the wireless range of an existing network or to extend internet connectivity to a remote location in a long range point to point link.
Here is a picture demonstrating repeater and access point topologies.
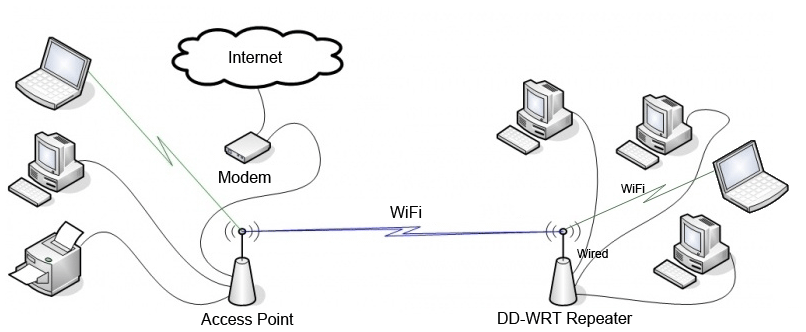
It is a common misconception that a WiFi repeater increases the signal of every wireless network that your laptop detects, but in reality a WiFi repeater such as implemented by DD-WRT will only connect to one distant wireless network at a time.
An implementation commonly used for a mobile repeater that needs to connect to many different networks is called an AutoAP. This is a configuration for Broadcom based DD-WRT routers where the unit will automatically detect and connect to the strongest open/unsecured WiFi signal in range in repeater mode. This method does not require you specify the network name to repeat, and is desirable for implementations such as a repeater in an RV visiting various campsites. It is not desirable to set up AutoAP when you are trying to establish a long distance point to point link, or for when the router is not going to be moved from place to place. For those implementations you would want to configure as a normal repeater.
A repeater bridge is essentially the same as a repeater, however a repeater bridge uses the DHCP server of the existing network so that all computers are on the same subnet. In most cases a normal repeater is fine and a more desirable setup, but some networks may have resources such as network storage or print servers that will not function correctly with devices on different IP networks.
To configure these modes, use the links at the top of the page under Broadcom and Atheros.
Another popular implementation is setting up a DD-WRT router as a VPN client. This use is becoming quite common as services such as Hulu and Netflix have became popular. These types of services can only be used in the United States, however. In order to circumvent this limitation, many people are using services such as StrongVPN when overseas to acquire a United States IP address, so that these services may be used. VPN is also used by many companies and universities so that users may access company resources from home. DD-WRT routers may be configured to use a VPN service so that any laptop or desktop connected to the router is connected to the VPN, and thus has the benefits of VPN connectivity. Setting up VPN requires an account with a VPN service. Usually, your VPN provider will have set up instructions specific to their service. In the DD-WRT setup pages you can configure the router as a VPN Client on the Services>VPN tab by enabling the appropriate client configuration.
Further modes and implementations are discussed on dd-wrt.com here.
A few more tips..
Feel free to explore the DD-WRT setup page on your own, but be sure to make a backup when you get a working configuration for your implementation. This is done under Administration>Backup and will allow you to restore your configuration in the event something goes awry.
If you really mess up the configuration or forget a password, you can always reset the unit back to the default configuration. This is done by powering up the unit, then holding the reset button on the back of the router with a pen for about 20 seconds or until the power light flashes at a regular interval. About a minute later the unit will have rebooted and be accessible again.
One thing that can mess up or 'brick' the router rendering it useless such that you cannot simply reset the unit is reflashing the unit with the wrong firmware. Typically there is no reason to reflash a router, unless you intend on using a specific firmware version or intend on using a firmware other than DD-WRT. Even then, the version shipped with your router is typically the best to use. It is a common misconception that it is best to upgrade the router to the latest version of DD-WRT, but in reality more recent versions may be more unstable and less functional than older versions which have undergone extensive testing and were developed specifically for the router upon which they are installed. If you intend to reflash the unit be absolutely sure you know what your doing, and have checked that you have selected a compatible version.